단원:
4. 객체 포인터와 객제 배열, 객체의 동적 생성
5. 함수와 참조, 복사 생성자
6. 함수 중복과 static 멤버
[실습 4.9]다음과 같은 Person 클래스가 있다. Person 클래스와 main()함수를 작성하여, 3개의 Person 객체를 가지는 배열을 선언하고, 다음과 같이 키보드에서 이름과 전화번호를 입력받아 출력하고 검색하는 프로그램을 완성하라.
코드:
| #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class person { string name; string tel; public: person(); string getname() { return name; } string gettel() { return tel; } void set(string name, string tel) { this->name = name; this->tel = tel; }; }; person::person() { } int main() { person info[3]; string nameinfo; string telinfo; cout << "이름과 전화번호를 입력해 주세요.\n"; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { cout << "사람" << i+1 << ">>"; cin >> nameinfo; //space 키가 들어올때까지 이름 입력 getline(cin, telinfo, '\n'); //엔터키가 들어올때까지 번호입력 info[i].set(nameinfo, telinfo); } cout << "모든 사람의 이름은 "; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { cout << info[i].getname() << " "; } cout << "전화번호 검색합니다. 이름을 입력하세요:\n"; getline(cin, nameinfo, '\n'); string namecheck; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { namecheck = info[i].getname(); if (namecheck == nameinfo) { cout << "전화번호는: " << info[i].gettel(); return 0; } } cout << "일치하는 정보 없음\n"; return 0; } |
결과:

[실습 4.13]영문자로 구성된 텍스트에 대해 각 알파벳에 해당하는 문자가 몇 개인지 출력하는 히스토그램 클래스 Histogram을 만들어보자.
대문자는 모두 소문자로 변환하여 처리한다.
코드:
| #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class histogram { string mainstring; int length; void changealphabet(); //대문자 -> 소문자 변환용 void counter(); //알파벳 숫자 세기 public: histogram(string c) //생성자함수 { this->mainstring = c; //클래스 메인스트링에 최초입력 문자열 추가 this->mainstring = mainstring + "\n"; } void put(string c) { this->mainstring = mainstring + c; } void putc(string c) //문자추가함수 { this->mainstring = mainstring + c; } void print(); //출력함수 }; void histogram::print() { cout << mainstring << endl << endl; changealphabet(); //대소문자 변환 counter(); char key = 'a'; for (key; key < 122; key++) //숫자를 셀 문자열 증가. 알파벳 z가 아스키코드 123임. { int alphabetnum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < this->length; i++) { //cout << mainstring[i] << " DEBUG " << endl; if (key == mainstring[i]) alphabetnum++; } cout << key << "(" << alphabetnum << ") : "; for (int i = 0; i < alphabetnum; i++) { cout << "*"; } cout << endl; } } void histogram::changealphabet() { string& refn = mainstring; //mainstring 의 문자를 직접 바꾸기 위해 레퍼런스 사용 this->length = mainstring.length(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (refn[i] >= 65 && refn[i] <= 90) refn[i] = refn[i] + 32; //아스키코드 변환 } } void histogram::counter() { //대소문자 변환이 종료된 후 사용할 것 int total = 0; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (mainstring[i] >= 97 && mainstring[i] <= 121) total++; } cout << "총 알파벳 수: " << total << endl << endl; } int main() { histogram elvisHisto("Wise men say, only fools rush in But I can't help, "); elvisHisto.put("falling in love with you"); elvisHisto.putc("-"); elvisHisto.put("Elvis Presely"); elvisHisto.print(); } |
결과:

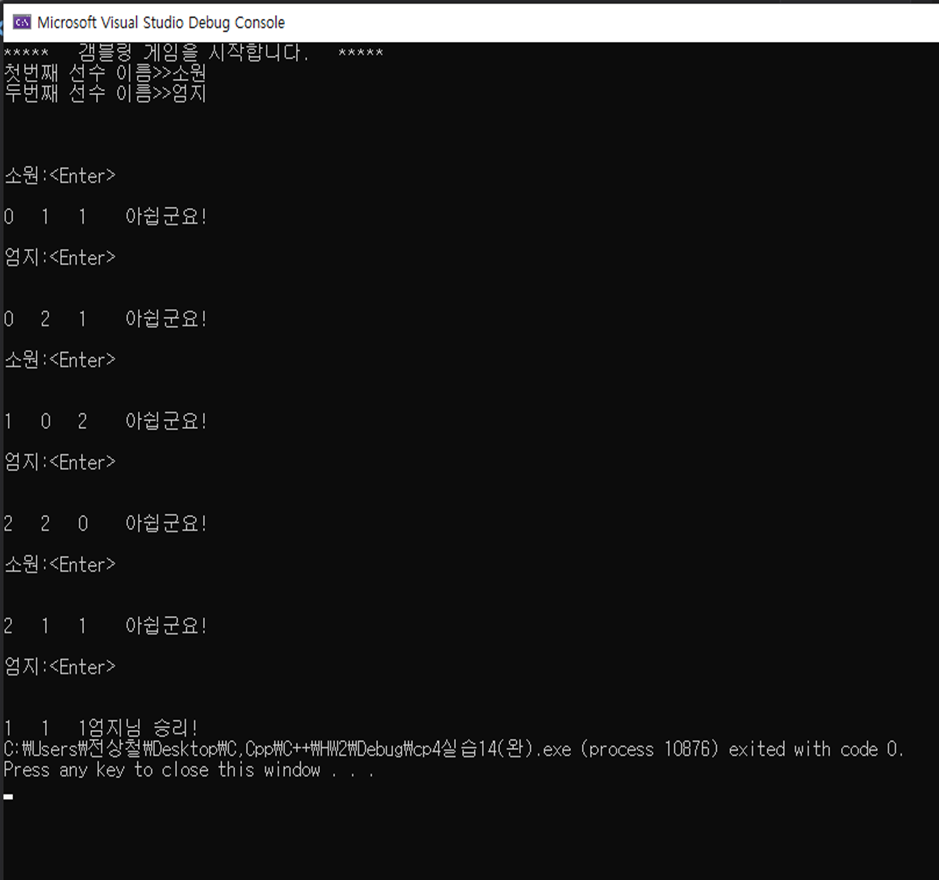
[실습 4.14]갬블링 게임 만들기. 두명이 게임을 진행하며 선수의 이름을 초기에 입력받고 자신의 차례에서 엔터를 누르면 랜덤수 3개가 생성되며 다 똑같은 숫자이면 게임에서 승리한다.
GamblingGame 클래스로 작성하라. 선수는 player클래스로 작성하고 2명의 선수는 배열로 구성하라.
코드:
| #include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<ctime> #include<string> using namespace std; class Player { public: string name; //플레이어의 이름 저장 void setPlayer(string name) //생성자함수 { this->name = name; } }; class GamblingGame { public: GamblingGame(); }; GamblingGame::GamblingGame() { cout << "***** 갬블링 게임을 시작합니다. *****" << endl; Player player[2]; //굳이 클래스 배열로 만들기위해 생성. string tmp; //선수명 저장 임시변수 int random[3]; //게임용 변수 cout << "첫번째 선수 이름>>"; cin >> tmp; player[0].setPlayer(tmp); cout << "두번째 선수 이름>>"; cin >> tmp; player[1].setPlayer(tmp); cout << "\n\n\n"; srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //랜덤시드 초기화 do { cout << player[0].name << ":<Enter>" << endl; cin.ignore(); //입력버퍼 비우기 getline(cin, tmp, '\n'); //엔터키 누르라길래.. random[0] = rand() % 3; random[1] = rand() % 3; random[2] = rand() % 3; cout << random[0] << " " << random[1] << " " << random[2]; if (random[0] == random[1] && random[1] == random[2]) { cout << player[0].name << "님 승리!"; break; } cout << " 아쉽군요!\n\n"; cout << player[1].name << ":<Enter>" << endl; cin.ignore(); //입력버퍼 비우기 getline(cin, tmp, '\n'); //엔터키 누르라길래.. random[0] = rand() % 3; random[1] = rand() % 3; random[2] = rand() % 3; cout << random[0] << " " << random[1] << " " << random[2]; if (random[0] == random[1] && random[1] == random[2]) { cout << player[1].name << "님 승리!"; break; } cout << " 아쉽군요!\n\n"; } while (1 == 1); } int main() { GamblingGame start; return 0; } |
결과:
[실습 5.5]다음과 같은 circle 클래스와 increaseby 함수가 있다. 함수가 잘 작동하도록 수정하라.
코드:
| #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Circle { int radius; public: Circle(int r) { radius = r; } int getRadius() { return radius; } void setRadius(int r) { radius = r; } void show() { cout << "반지름이" << radius << "인 원" << endl; } }; /* void increaseBy(Circle a, Circle b) { int r = a.getRadius() + b.getRadius(); a.setRadius(r); } */ void increaseBy(Circle &a, Circle b) { int r = a.getRadius() + b.getRadius(); a.setRadius(r); //Circle a를 직접 제어하기 위해 레퍼런스를 사용하였다. } int main() { Circle x(10), y(5); increaseBy(x, y); //x의 반지름이 15인 원을 만들고자 한다. x.show(); //"반지름이 15인 원"을 출력한다. } |
결과:

[실습 5.8]5번의 MyIntstack를 수정하여 다음과 같이 선언하였다.(교재 참고) 스택에 저장가능한 정수의 최대 갯수는 생성자에서 주어지고 size 멤버에 유지한다.
MyInStack클래스를 작성하라.
코드:
| #include<iostream> using namespace std; class MyIntStack { int* p; //스택 메모리로 사용할 포인터 int size; //스택의 최대 크기 int tos; //스택의 탑을 가리키는 인덱스 public: MyIntStack(); MyIntStack(int size); MyIntStack(const MyIntStack& s); //복사생성자 ~MyIntStack(); bool push(int n); //정수 n을 스택에 푸시 //스택이 꽉 차있으면 false, 아니면true 리턴 bool pop(int& n); //스택의 탑에 있는 값을 n에 팝한다. //스택이 비었으면 false, 아니면 true 리턴 }; MyIntStack::MyIntStack() { } MyIntStack::MyIntStack(int size) //스택 생성 { p = new int[size]; this->size = size; tos = -1; //아직 아무것도 없어서 tos는 -1 임 } MyIntStack::MyIntStack(const MyIntStack& s) //스택 복사시 실행할 생성자 { this->tos = s.tos; this->size = s.size; this->p = new int[size]; //데이터 복사파트 for (int i = 0; i <= tos; i++) { this->p[i] = s.p[i]; } } MyIntStack::~MyIntStack() //스택 소멸시 사용할 생성자 { delete[](this->p); } bool MyIntStack::push(int n) //푸시함수 { if (tos == 19) return false; tos++; //하나 저장할거니까 tos 1 증가 this->p[tos] = n; return true; } bool MyIntStack::pop(int& n) { if (tos == -1) return false; n = this->p[tos]; //tos 즉 탑에 저장된 데이터 팝 tos--; //하나 뺐으니까 tos 하나 증가 return true; } int main() { MyIntStack a(10); a.push(10); a.push(20); MyIntStack b = a; //복사생성 b.push(30); int n; a.pop(n); //스택 a 팝 cout << "스택 a에서 팝한 값 " << n << endl; b.pop(n); //스택 b팝 cout << "스택 b에서 팝한 값 " << n << endl; return 0; } |
결과:

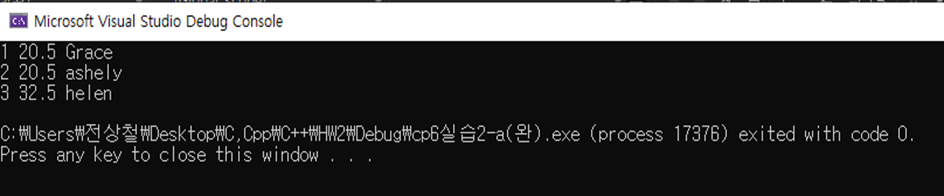
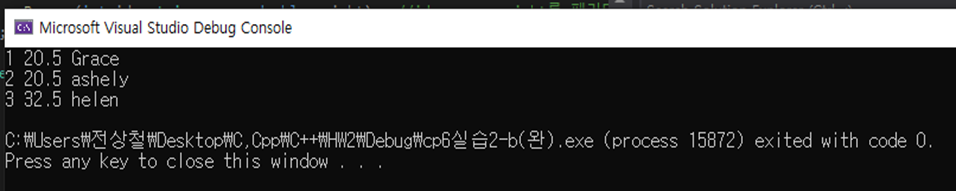
[실습 6.2]Person 클래스의 객체를 생성하는 main()함수가 주어진다.
(a)생성자를 중복 작성하고 프로그램을 완성하라.
(b)디폴트 매개변수를 가진 하나의 생성자를 작성하고 프로그램을 완성하라.
코드-a:
| #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Person { int id; double weight; string name; public: void show() { cout << id << ' ' << weight << ' ' << name << endl; } Person(); //패러미터 없는 생성자 Person(int id, string name); //id, name을 패러미터로 받는 생성자 Person(int id, string name, double weight); //id, name, weight를 패러미터로 받는 생성자 }; Person::Person() { this->id = 1; this->name = "Grace"; this->weight = 20.5; } Person::Person(int id, string name) { this->id = id; this->name = name; this->weight = 20.5; } Person::Person(int id, string name, double weight) { this->id = id; this->name = name; this->weight = weight; } int main() { Person grace, ashely(2, "ashely"), helen(3, "helen", 32.5); grace.show(); ashely.show(); helen.show(); } |
결과-a:
코드-b:
| #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Person { int id; double weight; string name; public: void show() { cout << id << ' ' << weight << ' ' << name << endl; } Person(int id = 1, string name = "Grace", double weight = 20.5); //id, name, weight를 패러미터로 받는 생성자 }; Person::Person(int id, string name, double weight) { this->id = id; this->name = name; this->weight = weight; } int main() { Person grace, ashely(2, "ashely"), helen(3, "helen", 32.5); grace.show(); ashely.show(); helen.show(); } |
결과-b:
문제 소스:
책정보, 명품 C++ Programming : 네이버 책 (naver.com)
명품 C++ Programming
C++는 1979년 BJARNE STROUSTRUP에 의해 “C WITH CLASSES”라는 이름으로 시작되었지만, 지금은 시스템 소프트웨어, 응용 소프트웨어, 게임, 임베디드 소프트웨어, 모바일 프로그램 등 소프트웨어의 전 분
book.naver.com
'프로그래밍 > C,C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [명품 C++ programming]9장 Open challenge (0) | 2022.01.06 |
|---|---|
| [명품 C++ programming]7,8,9장 실습문제 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [명품 C++ programming]2,3장 실습문제 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [ANSI C 프로그래밍]13장 프로그래밍 연습 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [ANSI C 프로그래밍]10장 프로그래밍 연습 (0) | 2022.01.06 |